Signs and Symptoms of Periodontal Disease (Gum Disease)
- Updated on: Jun 24, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
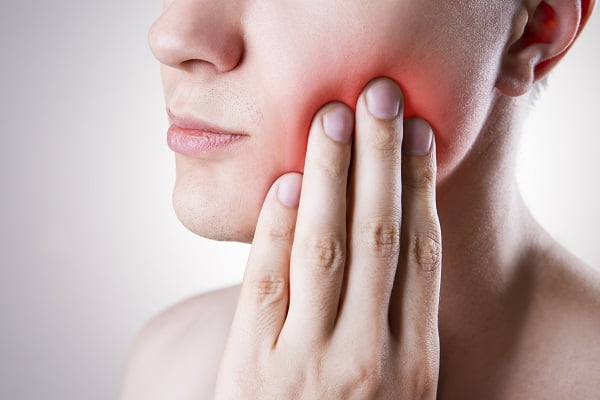
How do I know if I have gum disease?
Periodontal disease is a pathological condition that leads to teeth loss and bleeding gums in many people worldwide. It is the most common form of gum disease and can be prevented easily by taking care of your teeth and gums. Periodontal disease is further categorized as gingivitis and periodontitis.
Periodontal disease is caused by bacteria that release a toxin which irritates and inflames gum tissue (gingiva). It eventually leads to the destruction of gums and the underlying bone. If left untreated, periodontal disease can result in loss of teeth. Read about causes of gum disease.
Healthy gums are pink in color, firm and keep teeth securely in place. Most importantly, gums should not bleed during brushing.
Gum disease is generally painless, thus a person may not know he/she is suffering from this disease. It is often thought that brushing your teeth harshly can cause them to bleed. However, bleeding from gums is not normal in case of brushing and it should be taken as a warning sign.
Bad breath and abnormal taste are commonly associated with this disease.
Symptoms of gum disease
Initial symptoms of the gum disease include:
- bleeding gums after brushing and flossing teeth
- red and swollen gums
The above-mentioned symptoms are of gingivitis. As the disease progresses, root surface is exposed which may cause tooth sensitivity to temperature and pressure changes. The deep pockets are generally detectable by the probe used by dentists. As the pockets deepen, supporting bone loss takes place. The collection of pus in these pockets and swelling in gum result in pain and discharge from gum tissue.
As the drifting and loosening of teeth advances, it becomes difficult to eat. Initial signs of periodontitis include:
- swollen and tender gums
- persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- bright red, dusky red or purplish gums
- lose teeth that can make eating difficult
- unpleasant taste in mouth
- collection of pus under gums and teeth (gum abscesses)
- a change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
Following are the symptoms that need dental attention immediately:
Pain and swelling
The early signs of gum infection include redness and swelling in gums for no apparent reason. It is important to stop the infection before it could extend up to the teeth base and jaw bone.
Bleeding gums
Bleeding from gums and teeth while eating, brushing and flossing is another major sign that should not be ignored. The toxins released by bacteria present in the plaque make gum tissue sore and tender which causes them to bleed.
Receding gums
Periodontal disease leads to recession of gums and longer-looking teeth. The toxins produced by bacteria destroy the supporting tissue and gums making the teeth look bit longer than normal. The smile of the person suffering from the periodontal disease may look bit “toothy”.
Bad breath
Mouth odor may originate from the back of tongue, lungs and stomach. It may also be because of food we eat or from tobacco. However, the periodontal disease also causes bad breath (halitosis).
The food we eat mixes with saliva and sits in the deep pockets of receding gums, between the teeth and underneath the gum line. Bacteria thrive and multiply on this food debris and cause a foul odor.
Change in teeth pattern
Spread of periodontitis causes once firmly fixed teeth to loosen up a little bit. The damage of gum tissues and bones by the bacteria change the pattern of teeth and make them shift positions.
Pus formation
A yellow-colored liquid called pus oozing out of gums (or teeth) is a definite and serious sign of periodontal disease.
Gum diseases are silent and symptoms may not appear until it advances to later stages. It is important to note that gingivitis may progress into periodontitis without any warning sign or symptom. Thus, dentists recommend regular dental check-ups.
Treatment of infection before it is carried to other parts of the body through the bloodstream is quite important. Read about treating the gum disease.