Treatment for Lupus
- Updated on: Jun 12, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Oct 2, 2019


Lupus, an autoimmune disease shows a variety of signs and symptoms. It is always advised to consult a doctor or physician to treat lupus. Careful discussion about benefits and risks of treatment should be considered before taking up any treatment.
Following are the most commonly used medication for the treatment of lupus:
- Anti-inflammatory (over-the-counter pain relievers)
- Anticoagulant drugs
- Antimalarial drugs
- Corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressants
- Monoclonal antibodies
These treatments are discussed in details below.
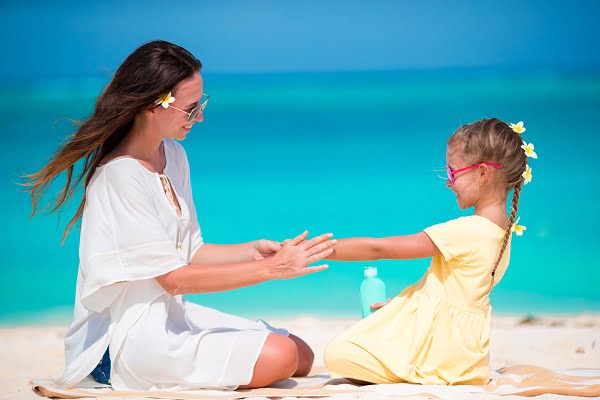
Protecting yourself from the sun
Exposure to sunlight can worsen your lupus symptoms, in particular skin rashes. It’s important to protect your skin. Read about lupus signs and symptoms.
You may prefer:
- using clothes that covers your skin
- keeping a hat
- to wear sunglasses
- to apply sunscreen
People get most of their vitamin D needed by the body from direct sunlight. There’s a risk you may not get enough of vitamin D if you are avoiding sun exposure. Therefore, it may be a good idea to supplement this from vitamin sources such as foods and other supplements.
This will help prevent diseases such as osteoporosis.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Anti-inflammatory medicines reduce pain and inflammation – the main symptoms of lupus. These are the common drugs which are used to treat symptoms like fever and arthritis.
In the early stages, use of anti-inflammatory medicines is the only treatment needed by the person suffering from lupus.
Some anti-inflammatory drugs with their possible side effects are given below:
Aspirin
Aspirin is a pain reducer with anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant properties. It helps in thinning of blood and can easily control symptoms of lupus. However, it can cause stomach irritation.
Acetoaminophen
Acetoaminophen is also used for lupus treatment. It can control pain to a certain extent, and causes less stomach irritation as compared to aspirin. However, it does not have any effect on inflammation. In general, it does not have any side effect but some cases of acute liver failure have been reported.
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a known inflammation suppressant that relieves joint pain and stiffness but it may cause stomach irritation in some people.
These are non-steroidal medicines with no or very fewer side effects and are commonly available by prescription.
People often respond to one or the other type of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in a better way. These medicines are taken with food, milk or antacid or may be accompanied with other medicines.
In spite of this, the main concern with these drugs is the severe gastrointestinal problems they cause like stomach irritation, bleeding, ulcer etc.
Excessive use of these drugs can also reduce the blood flow to kidneys and interfere with their ability to remove wastes from the body. Keeping in view the complications that are caused by these drugs, the medication is stopped as symptoms go away.
Anti-coagulant medicines
Blood clots can be a life threatening symptom of lupus. Anticoagulant drugs have a property of thinning blood thus preventing any clot formation.
Heparin (Calciparine® and Liquaemin®) and warfarin (Coumadin®) are commonly prescribed by doctors. A low-dose of aspirin also works as an anticoagulant.
Side Effects
Time to time monitoring is required if the person is being treated with warfarin to make sure that the blood does not become too thin. A recent study shows that genetic makeup of a person could influence the way they respond to warfarin. Therefore, the dosage may vary from person to person. Anticoagulant therapy may go lifelong for some people.
Antimalarial drugs
Antimalarial medicines are very commonly used to control lupus. These drugs are available on prescription and are used in combination with other medicines.
Generally two types of antimalarial drugs are prescribed- hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil®) and chloroquine (Aralen®).
Though these medicines are often prescribed for mouth ulcers, skin rashes and joint pain, they are also effective in reducing inflammation and blood clotting. Antimalarial drugs control lupus by protecting against damages caused by ultraviolet radiations and by reducing the level of autoantibody.
Side effects
Side effects of antimalarial drugs are rare or mild which go away as soon as the body adjusts to the drugs.
Common side effects are stomach irritation and changes in skin color. With low doses of antimalarial drugs, the risks of complications are low. However, if taken in very high doses, retinal damage which causes vision problem may take place.
A baseline examination as a precaution is done before treating people with antimalarial drugs. Pregnant women suffering from lupus are advised to continue their medications.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids (aka glucocorticoids, cortisone or steroids) are synthetic prescription drugs. These drugs are designed to work like the naturally occurring hormone produced by the adrenal gland in the body.
These are steroid-based medicines that work by reducing swelling, warmth and pain associated with pain. Prednisolone and methylprednisolone (Medrol®) are the most commonly prescribed corticosteroids.
Corticosteroids are taken orally in the form of pills.
Creams and gels are also available and are used for skin lupus. In some cases of skin lesions, corticosteroids in liquid form are injected into muscles and directly into joints.
The most beneficial effect is shown by pulse steroids that are intravenously injected into a nerve.
Side effects
Doctors and physicians try to keep the dosage at the lowest effective level. This is due to the various side effects caused by steroids. Some common side effects are:
- Ance
- Weight gain and hair growth
- Fragile skin that bruises easily
- Suppressed growth in children
- Irritability, agitation, excitability, insomnia or depression.
Apart from above-mentioned side effects, corticosteroids have some long term effects. These long term effects are:
- increased risk of infections (a person should take extra care to clean and protect open wounds)
- avascular necrosis of bone ( quite painful and mostly in the hip region)
- osteoporosis (bones become fragile and prone to fractures)
- muscle weakness and cataracts.
Immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressants are the drugs that suppress the immune system and are helpful in extreme cases of lupus.
The most often prescribed drugs are azathioprine (Imuran and Azasan), mycophenolate (CellCept), leflunomide (Arava) and methotrexate (Trexall). These medications are prescription drugs used to control inflammation and hyperactive immune system.
Side effects
In general, these medications are prescribed in the cases when steroids are unable to reduce the symptoms or the patient is not able to tolerate high doses of steroids. However, these drugs do have potential side effects like liver damage, decreased fertility and increased risk of cancer.
People taking these drugs to control lupus should be carefully monitored from time to time as these drugs reduce the ability to fight infections and chances of getting a viral infection increase.
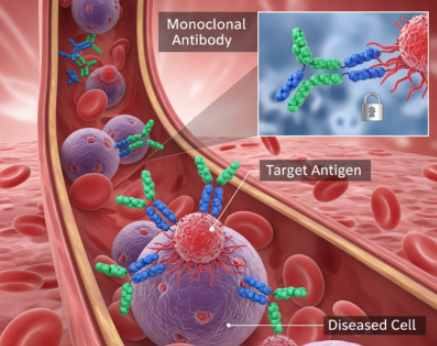
Monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies were developed to disrupt the activation of B-cells against any antigen.
They interfere with BLyS protein which is required for B-cell activity. Benlysta is the first and the only drug specifically developed for and approved to treat lupus.