Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- Updated on: Jul 12, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Feb 21, 2021
Most kidney ailments don’t have a particular medication treatment. The primary objective in treating kidney illness is to address the fundamental reasons for the sickness and prevent the infection from advancing. This implies treating conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure/ hypertension. Therefore, depending on the underlying cause, some types of kidney diseases can be treated. Though, chronic kidney disease often has no cure.
Treatment for the Cause and Complications
Hypertension – Patients with high blood pressure/ hypertension, should take blood pressure medications and embrace a sound eating diet and exercise schedule. Those with intense diseases, for example, urinary tract contamination, ought to be treated with anti-toxins or have any obstructions in the urinary tract expelled.
Anemia — People with CKD are at hazard for weakness. This happens because improperly functioning kidneys produce reduced amounts of a substance called erythropoietin. Anemia can prompt weakness and inconvenience. Chosen patients can be treated with drugs that empower the generation of red platelets.
Dietary changes — Changes in your eating routine might be prescribed to control or prevent some of the complications of CKD; the most imperative is salt limitation to help control the blood pressure.
Protein — Restricting protein in the diet may moderate the progression of CKD, even though it is not clear if the advantages of protein limitation are justified regardless of the trouble of adhering to a low-protein slim down. Even though a decreased protein eating regimen may defer dialysis for quite a while, the unappetizing idea of the eating routine is troublesome for the vast majority to endure.
Potassium — Some individuals with CKD build up a high blood potassium level, which can interfere with normal cell function. This is as often as possible treated with a diuretic. Measures to counteract high potassium may likewise be suggested, including a low-potassium eat less carbs diet and avoiding medicines that raise potassium levels.
Cholesterol and triglycerides — High cholesterol and triglyceride levels are basic in individuals with kidney infection. High triglycerides have been related to an increased risk of coronary artery disease, which can lead to heart attack.
Medications to manage swelling — People with chronic kidney disease may easily retain fluids (such as water) in the body which can lead to swelling in the legs and high blood pressure. Diuretics are medications that can help maintain fluid balance in your body.
Medications to protect your bones — Your doctor may suggest calcium and vitamin D supplements to prevent weak bones and lower your risk of osteoporosis and fracture. You may also take medication such as phosphate binder to lower the amount of phosphate in your blood and protect your blood vessels from damage by calcium.
The medical care of patients with CKD should focus on the following aspects:
- Delaying or stopping the progression of CKD
- Diagnosing and treating pathologic manifestations of CKD
- Planning for a long-term treatment plan if needed in future – renal replacement therapy
Treatment for end-stage kidney disease
For patients with stage 5 CKD, the function of the kidneys is significantly compromised, and cannot normally keep up with daily demands. For this reason, patients will frequently require kidney dialysis or a transplant to survive.
Kidney Dialysis
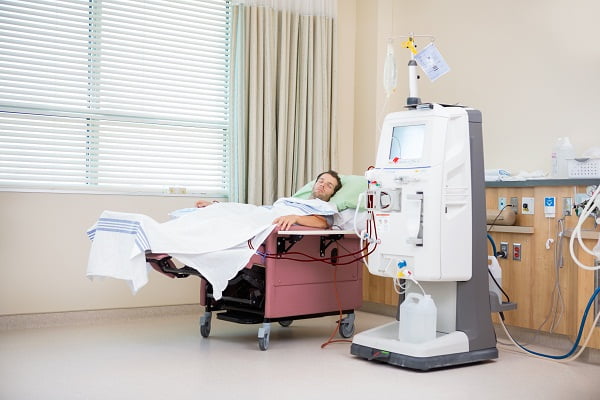
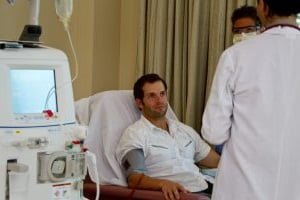
Dialysis is an artificial way of cleaning your blood. It uses an artificial kidney system, known as a hemodialyzer, to remove waste matter and chemicals from your blood. Your doctor will surgically create a vascular access, or an entrance point, into your blood vessels to get the blood to flow to the artificial kidney. This access will allow a larger amount of blood to flow through your body during hemodialysis treatment. This means more blood can be filtered and purified.
Hemodialysis treatments usually last three to five hours. The treatment is generally required three times per week. However, hemodialysis treatment can also be done in shorter, more frequent sessions as per medical requirements.
Most hemodialysis treatments are done at a hospital, doctor’s office, or at a dialysis center. The length of treatment depends on your body size and the amount of waste in your body.
Kidney Transplant
While dialysis can get rid of waste products from your body, it does not replace all the functions of your kidneys. A transplant does that. It is a surgical technique in which a donor kidney from a live or deceased donor is placed into a person whose kidneys no longer function properly to treat the kidney damage.
Transplantation is a preferred treatment over dialysis because of its improved outcomes. However, finding a kidney donor is not easy.
FAQs
Can dialysis be avoided in chronic kidney disease?
In some cases, early intervention and lifestyle changes can slow the progression, delaying the need for dialysis. However, individual responses vary.
How does medication help manage chronic kidney disease?
Medications control blood pressure, treat anemia, and manage underlying conditions contributing to CKD. Compliance with prescribed medications is crucial for effective management.
What dietary changes are recommended for chronic kidney disease patients?
A renal-friendly diet involves controlling salt, phosphorus, and potassium intake. Consulting a dietitian can help tailor a diet plan that suits individual needs and preferences.
Can kidney transplantation cure chronic kidney disease?
Kidney transplantation can be a cure, providing a new, functioning kidney. However, it requires a suitable donor and lifelong post-transplant care.
How does exercise contribute to chronic kidney disease management?
Regular exercise improves overall health and can help manage conditions like hypertension and diabetes, contributing to better CKD management.