Understanding Metastatic Stomach Cancer
- Updated on: Aug 3, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Dec 14, 2021
Metastatic Gastric Cancer (Metastatic stomach cancer or MGC)
In a report by the World Health Organization (WHO), about 720,000 cancer-related deaths occur due to stomach cancer annually worldwide. Stomach cancer is supposed to be the fifth most common type of cancer in the world and is also estimated to be the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. With changes in diet and other lifestyle factors, the risk of developint stomach cancer has increased compared to what it was in the past.
Though the prognostic significance of age, sex, or ethnicity in metastatic gastric carcinoma is still unknown. It is also observed that most people diagnosed with stomach cancer either already have metastasis or have a great risk of developing it eventually. A metastatic cancer, or metastatic tumor, is one which has spread from the primary site of origin (where it first started) into anywhere in the body. It is an advanced state of the stomach or gastric cancer.
Metastatic Gastric Adenocarcinoma: Its association with Stage IV stomach cancer
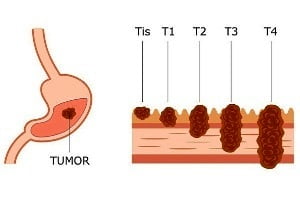
When stomach cancer spreads to the areas located near the stomach, it is referred to as regional metastasis and when it spreads to organs or parts that are far away from the stomach, it is known as distant metastasis. Sometimes, recurrent stomach cancer may also be counted as metastatic stomach cancer because distant metastasis (returning back of primary cancer back in another part of the body) might be observed when cancer has reoccurred after a few years.
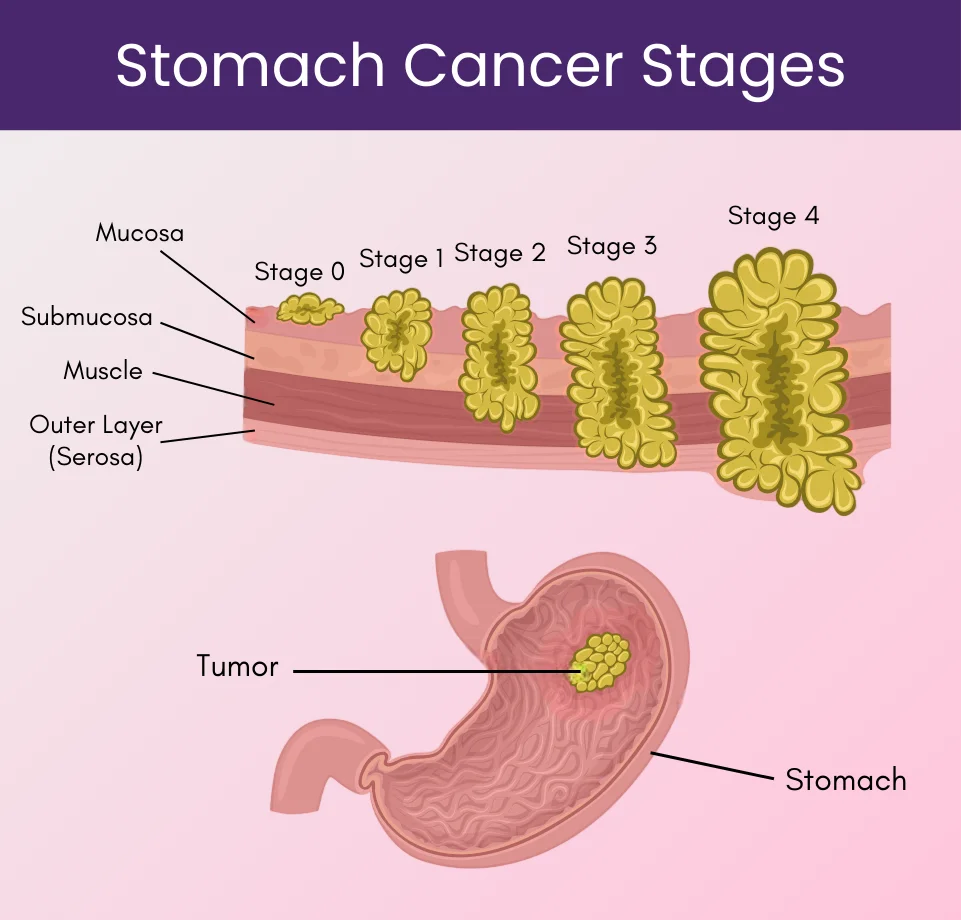
According to the ‘stages of stomach cancer’ defined by the American Cancer Society, metastatic gastric cancer occurs at stage 4 because stomach cancer, at this stage, spreads to the distant organs such as the liver, lungs, brain, or the peritoneum (the lining of the space around the digestive organs).
Stage IV stomach cancer is the most advanced form of stomach cancer and it cannot be cured. This type of cancer is very hard to treat but the treatment helps to keep the cancer under control, improves quality of life of patients and also helps to minimize the symptoms of stomach cancer.
Diagnosis: How do we detect metastatic stomach cancer?
In stage 4, when cancer (which primarily started in the stomach) has spread to farther parts of the body, it is diagnosed as metastatic stomach cancer or metastatic gastric cancer (MGC). Common organs affected by MGC are liver, lungs, lymph nodes, and bones. If the stomach cancer has metastasized to lungs, it can be referred to as stomach cancer with lung metastasis.
Treating metastatic gastric carcinoma
Doctors suggest that for metastatic cancer, a patient requires systemic therapy. Medications should be given orally or injected into the bloodstream to reach the cancer cells throughout the body, such as via chemotherapy or hormone therapy.
Surgery is not a recommended treatment for metastatic stomach cancer. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can prove to be beneficial to help shrink the tumor or cancer. A combination of these two therapies is also preferred in some cases. In a few cases, targeted therapy is also recommended if there is no positive effect of any other therapy and the condition worsens. In a small number of cases, doctor might recommend surgery if the bleeding or blockage occurs.
Surviving metastatic stomach cancer
The survival of patients with gastric cancer depends on the extent of the tumor. It was estimated by some researchers of Keck School of Medicine, United States, that men are twice at the risk of metastatic stomach cancer and death from it as compared to women. This study also suggested that median overall survival in stomach cancer patients with MGC was only 4 months.