What Are Hemorrhoids?
- Updated on: Jun 12, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Oct 2, 2019

Overview of hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are vascular structures present in the anal canal. In normal condition, hemorrhoids work as cushions that help in bowel control.
At times, the walls of these blood vessels stretch in a way that veins bulge out. This happens especially during the bowel movement. When these veins present in anus and rectum get inflamed and swollen, they cause a disease called as piles (or hemorrhoids). The term “hemorrhoids” may be misleading sometimes.
 Hemorrhoids are quite common worldwide. About 50-60% of the world’s population has hemorrhoids at some point in time in their lives. Men and women are affected equally with this condition.
Hemorrhoids are quite common worldwide. About 50-60% of the world’s population has hemorrhoids at some point in time in their lives. Men and women are affected equally with this condition.
Often people between the age group of 45-65 years are affected. Sometimes there is no noticeable symptom but most of the time they cause discomfort, itching and bleeding.
What causes hemorrhoids?
The exact cause of hemorrhoids is still unknown but a number of factors contribute to it. The common reasons for developing hemorrhoids are persistent constipation, diarrhea and sitting in the toilet for a long time. Read more about diagnosis of hemorrhoids.
Read more about treatment of hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids are a common condition that can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms. These symptoms can be broadly categorized into four main categories:
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids:
Bleeding during bowel movements:
This is a common symptom of hemorrhoids, particularly internal hemorrhoids. The bleeding may be bright red or dark and may be noticed on toilet paper, in the toilet bowl, or on the surface of the stool. Although the bleeding may be alarming, it is usually not serious and can be managed with appropriate treatment.
Pain or discomfort:
This is another common symptom of hemorrhoids. The pain may be felt as a dull ache or a sharp, stabbing pain in the anal area. The discomfort may be particularly severe during bowel movements or when sitting for extended periods of time.
Swelling around the anus:
This is also common with hemorrhoids and can make it difficult to sit comfortably. The swelling may be accompanied by a feeling of fullness or pressure in the rectal area.
Itching or irritation:
This is another common symptom of hemorrhoids. It can be caused by swollen and inflamed veins rubbing against the skin, as well as by the use of harsh soaps or toilet paper.
Types of Hemorrhoids
- Internal Hemorrhoids: These are located inside the rectum and are not visible from outside the body. Internal hemorrhoids may bleed, prolapse (protrude outside the anus), or become inflamed and painful.
- External Hemorrhoids: These are located under the skin around the anus and are visible from outside the body. External hemorrhoids may cause itching, irritation, and pain.
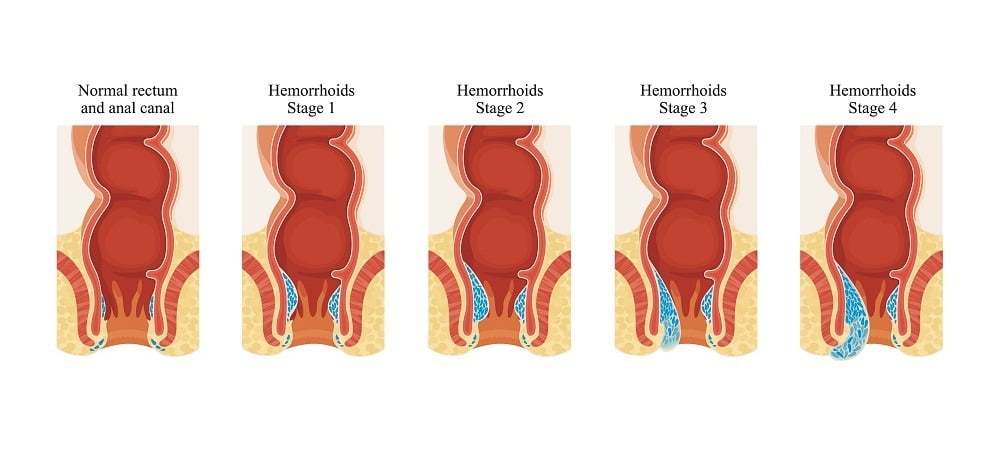
It is important to note that hemorrhoids can also be classified based on their severity, ranging from first-degree (mild) to fourth-degree (severe) hemorrhoids. Treatment options may vary based on the type and severity of hemorrhoids.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available for individuals suffering from hemorrhoids. Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, medications, or procedures, depending on the severity of the condition.
A. Lifestyle Changes
- High-fiber diet: A high-fiber diet can help prevent constipation and straining during bowel movements, which can aggravate hemorrhoids. Foods high in fiber include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can also help prevent constipation and promote healthy bowel movements. Exercise can also help maintain a healthy weight, which can reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
B. Medications
- Topical creams: Over-the-counter creams and ointments can be applied to the affected area to help relieve pain and itching. These creams typically contain ingredients such as hydrocortisone, witch hazel, or lidocaine.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with hemorrhoids.
C. Procedures
- Rubber band ligation: This procedure involves placing a small rubber band around the base of the internal hemorrhoid, cutting off the blood supply and causing hemorrhoid to shrink and eventually fall off.
- Sclerotherapy: This involves injecting a chemical solution into a hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink and eventually disappear.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: This is a surgical procedure that involves removing the hemorrhoid tissue. This procedure is typically reserved for severe or persistent hemorrhoids that have not responded to other treatments.
In addition to these treatment options, prevention is key in managing hemorrhoids. Maintaining a healthy weight, drinking plenty of fluids, exercising regularly, and avoiding straining during bowel movements can all help prevent hemorrhoids from developing or worsening.
Prevention of Hemorrhoids
Preventing hemorrhoids is essential to avoid the discomfort and pain associated with this condition.
To reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids, individuals can take the following steps:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the veins in the anal area.
- Drink plenty of fluids to keep stool soft and easy to pass, reducing the need for straining during bowel movements.
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation and maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid straining during bowel movements by maintaining a high-fiber diet, drinking plenty of fluids, and taking time to fully evacuate the bowels.
By following these simple steps, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing hemorrhoids and improve their overall quality of life.












