What Are the Causes and Risk Factors of Osteoarthritis?
- Updated on: Jun 12, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Oct 2, 2019
What Causes Osteoarthritis?
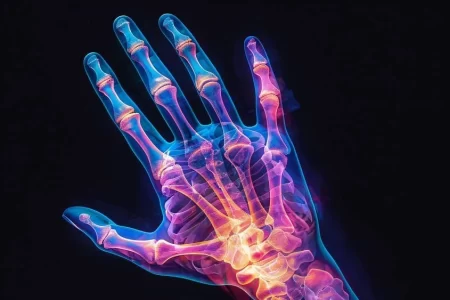
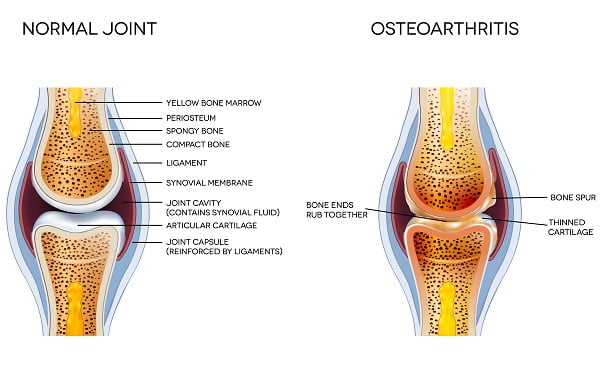
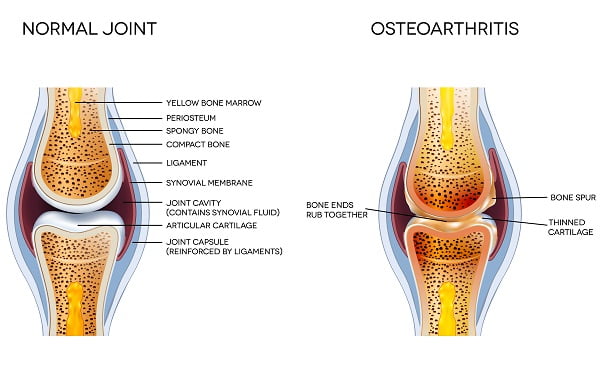
Every joint has a natural shock absorber called cartilage. Cartilage is smooth, elastic, rubber like material that acts as cushions at the end of the bones. It reduces the friction between two bones, making them work smoothly.
As people age, their joints become stiff and cartilage becomes more susceptible to wear and tear. The continuous use of joints starts damaging the cartilage and as a result, the bones start rubbing against one another, causing pain and swelling.
What are the Causes of Primary osteoarthritis?
Primary osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that comes naturally with increasing age. As the age progresses, the protein content of cartilage degrades and its water content increases drastically.
Continuous use of joints over the years severely damages the cartilage causing extreme joint pain and swelling. The loss of cartilages results in friction between bones which enhances pain and decreases joint mobility. This damage in the cartilage can also promote new outgrowth near the bones.
Primary osteoarthritis can normally be found in the members of a family via inheritance. The exact reason of primary osteoarthritis is not known.
What are the Causes of Secondary osteoarthritis?
Another type of osteoarthritis, known as secondary osteoarthritis, is usually caused due to some other disease or conditions (risk factors of osteoarthritis).
- Diseases such as protrusio acetabuli, post traumatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, etc are the main causes of secondary osteoarthritis. In secondary osteoarthritis, the exact cause of the disease is known.
- Some people are born with deformed joints that make them more susceptible to mechanical wear and tear. This results in degradation and loss of cartilage. This also results in secondary osteoarthritis.
- Disturbances in hormones, such as growth hormones, etc also results in secondary osteoarthritis.
- Deposition of crystals in the cartilage such as uric acid crystals, calcium pyrophosphate crystals can also cause secondary osteoarthritis.
- Apart from diseases, there are many other factors like trauma, injury, genetic factors, inflammation of joints, etc that can result in secondary osteoarthritis.
What are the Risk factors of osteoarthritis?
There are certain risk factors that can result in the occurrence of osteoarthritis. Some of them are:
Weight
Our joints are very important not only because they help in movement but also carry body weight. Excess of weight exerts an extra pressure on joints and damages the cartilage more quickly. This increases the risk of osteoarthritis in obese people.
Injury
Continuous body movements and injuries to joints like fracture, surgery or ligament damage can cause osteoarthritis.
Sports people are at a higher risk of developing osteoarthritis because they repeatedly damage their joints, ligaments and tendons. This accelerates the process of cartilage damage, thus causing osteoarthritis.
Joint overuse
Overuse of joints causes damage to cartilage and further results in osteoarthritis. People, who choose career path in which they have to bend repetitively, lift heavy weights, stand for a long period of time, etc, are more prone to cartilage damage and occurrence of osteoarthritis.
Can Genetics increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis?
There are many genetic factors that increase the risk of osteoarthritis in a person. For example, a rare defect in the production of collagen in body, a protein that forms cartilage, can result in osteoarthritis in young people.
If there is a slight defect in the position of bones due to inherited traits, the cartilage can be damaged severely. This can also result in the occurrence of osteoarthritis.
According to researchers, a gene called FAAH, that is linked to increase in pain sensitivity, is more in people with osteoarthritis than in normal people.