What Are the Causes of Diabetes?
- Updated on: Jun 12, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Oct 2, 2019
Diabetes is a chronic disease of metabolism. There are a variety of causes depending on your genetic makeup, family history, race, environmental factors, and your overall health.
There is no common cause for every type of diabetes because the causes of diabetes vary depending on the individual and the type of diabetes you have. Read about diabetes and its various types.
Type 1 Diabetes Causes
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system destroys your cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. This causes the pancreas to not produce enough insulin for the body to function properly. This is an autoimmune disorder because the body attacks its own immune system.
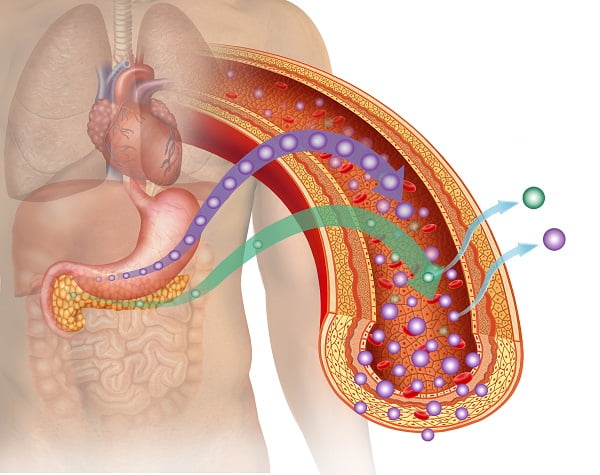
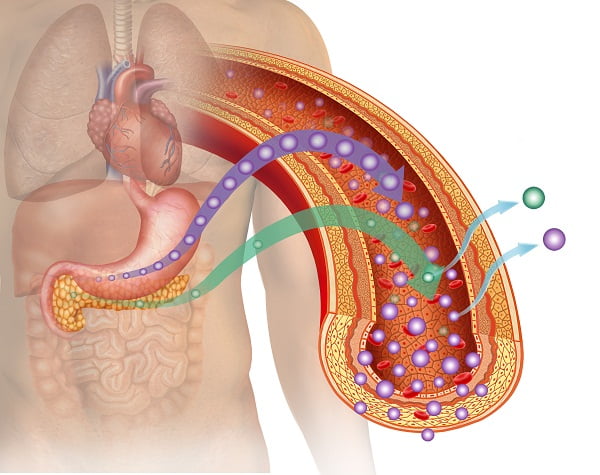
Type 1 diabetes illustration, anatomical image of the human body, highlighting organs such as the stomach and pancreas producing glucose with insufficient amount of insulin.
There is no particular cause of type 1 diabetes, but the following things are considered triggers and risk factors:
Family History
Family history is an important risk factor in some cases of type 1 diabetes. If you have a family member with type 1 diabetes, your risk of developing the condition increases. However, not everyone who is at risk for type 1 diabetes develops it. Scientists say that there may be other factors that trigger the condition.
Race
Race is another risk factor for type 1 diabetes. White individuals develop it more often than people of other races.
Other risk factors of type 1 diabetes
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Toxins with food
- Certain unidentified components that may cause autoimmune reactions
Type 2 diabetes causes
It is responsible for about 95% of diabetes cases in the United States, according to the CDC. The causes of type 2 diabetes are many and usually more than one cause is involved in the development of the condition. Often, the most important factor is a family history of type 2 diabetes. If you have someone with the disease in your family, you are at high risk of it.
Its various causes are listed below.
Age
Your risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases as you grow older.
White people over the age of 40 are at higher risk of developing it. People of south Asian, Chinese, African-Caribbean and black African races have higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in an early age.
However, over the recent years, even younger people from all ethnic groups have been developing the disease.
It is seen that children as young as six years develop type 2 diabetes, in some cases.
Genetics
Type 2 diabetes can be hereditary. In fact, it is a major risk factor. But that doesn’t mean that if your mother or father had type 2 diabetes, you’re sure to develop it. Instead, you have a greater chance of developing it.
Scientists know that type 2 diabetes is genetically linked, but it’s not known which genes carry the risk. Research is going on to understand certain genetic mutations that may lead to a risk of type 2.
NIH mentions that the disease tends to run in families and occurs more often in these ethnic groups:
- African Americans
- Alaska Natives
- American Indians
- Asian Americans
- Hispanics/Latinos
- Native Hawaiians
- Pacific Islanders
Lifestyle
Genes play a significant role in type 2 diabetes, but your lifestyle is extremely important. It is believed that even if you have a genetic mutation that may make you vulnerable to type 2 diabetes, taking care of your body well and maintaining a proper lifestyle may avoid its development or progression.
Certain lifestyle choices that affect the development of type 2 diabetes are:
- Lack of exercise: Physical activity can help you avoid type 2 diabetes, even if you’re susceptible to it.
- Living a sedentary lifestyle
- Obesity
- Unhealthy diet
Being Overweight/Obesity
Lack of exercise and unhealthy meal choices can cause obesity. Being overweight puts you at risk of many diseases including diabetes. You are more likely to become insulin resistant and can also get many other health conditions.
According to UK norms, people with a body mass index (BMI) of:
- 25 or above are considered overweight
- 30 or above are considered obese
However, some people are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes:
- Asians with a BMI score of 23 or more are at high risk of developing the disease
- Asians with a BMI of 27.5 or more are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes
In particular, fat around your tummy (abdomen) increases your risk of developing it. This is because it releases certain chemicals that can disrupt your body’s cardiovascular and metabolic systems.
According to NHS UK, some groups are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, based on their waist measurements. These considerations are presented below:
- women with a waist size of 80cm (31.5 inches) or more
- Asian men with a waist size of 89cm (35 inches) or more
- white or black men with a waist size of 94cm (37 inches) or more
Insulin Resistance
If your body is insulin resistant, it doesn’t use insulin properly which leads to diabetes. In fact, genetic susceptibility and lifestyle choices lead to insulin resistance only.
Your body though may produce enough insulin, but the body resists that insulin. Glucose builds up in the blood causing the symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
Read about signs and symptoms of diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy. Scientists believe that it is caused due to hormonal changes during pregnancy along with genetic and lifestyle factors.
During a pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones to sustain your pregnancy. These hormones may make your cells more resistant to insulin.
If you get diabetes while you are pregnant, it increases your risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in your life.












