What Are the Complications of Endometriosis?
- Updated on: Jul 9, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Sep 27, 2019

What happens when you have endometriosis?
Women suffering from endometriosis sometimes go through a number of complications like fertility problems and ovarian cysts. Having a problem in conceiving a child and keeping it to the terms is a serious complication associated with endometriosis.
Is there a cure for endometriosis?
Currently, there is no cure for endometriosis and medications cannot improve the damage done by this condition. Some women are though, able to conceive after removal of endometrial implants surgically.
Healthcare assistance is required before and during pregnancy. In some cases, this doesn’t work and the person may have to consider other options for having a baby.
Endometriosis complications
Following are the complications associated with endometriosis:
- Infertility
- Ovarian cysts
- Adhesion of organs
- Urinary and bowel complications
- Surgery complications
Infertility
Endometriosis, an estrogen-mediated disease can damage fallopian tubes and ovaries. This is a complication and can cause fertility problems. However, it is estimated that more than 50% of women suffering from mild and moderate endometriosis can get pregnant without any medical assistance. For rest of the women, medications do not improve the fertility but surgery to remove the endometrial implants can help.
In-vitro fertilization can be an option for women having trouble in conceiving the child.
It is possible that the endometrial implant will change the hormonal and chemical composition of the peritoneal fluid (fluid surrounding the abdominal cavity). This changes the menses cycle of the women and can prevent conceiving.
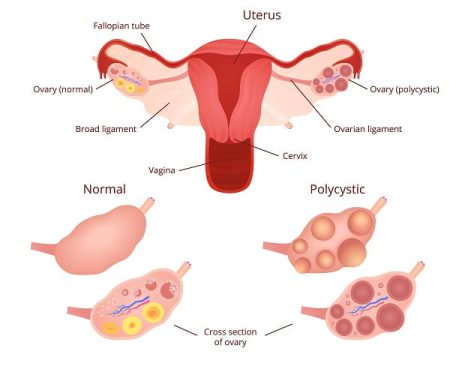
Ovarian cysts
Another major issue associated with endometriosis is the development of cysts in ovaries. Endometrial cysts are blood-filled growths and called as the endometrioma. The size of the cysts ranges widely with smallest being 1mm and largest being 8cm in diameter.
The symptoms of ovarian cysts and endometriosis can overlap. Moreover, some doctors have also reported that the risk of ovarian cancer is higher in women with endometrial cysts.
Adhesion of organs
Another complication with endometriosis is adhesion of organs. Endometriosis tissue growth in the outer areas of internal organs causes them to stick. This generally occurs when tissue growth is near or in ovaries.
Adhesion takes place in the places of implants and could change the shape (and/or function) of the organ. Generally, the only option left for its treatment is surgery.
Urinary and bowel complications
Endometriosis involving bladder and bowel can be at times difficult to treat. Major surgery is required in order to treat the patient for the symptoms. Surgery may involve cutting and removal of a part of bladder.
Apart from this, a tube called a catheter, is inserted in the bladder to help the patient with urination.
In few cases, a bag may be attached with a small hole in the abdomen area. This procedure is temporary and called as urostomy.
As bowel is also affected with severe endometriosis, a portion may be removed during surgery. During the healing time of bowel, women are given temporary colostomy. Just like urostomy, a bag is attached with a hole in abdomen and bowel is diverted through it.
Surgery complications
Like all other surgeries, endometrial surgery also has some complications which can be serious and sometimes even fatal for the patient. The most common ones are listed as:
- Wound infection
- Minor bleeding from surgery
- Bruising of wound
The above-mentioned complications are minor ones and somewhat common. Other serious complications include:
- Damage to internal organs
- Accidental hole or puncturing of womb, bladder and bowel
- Major bleeding
- Blood clot formation
To avoid complications, the patient should talk to the doctor prior to it and discuss the benefits and the risks involved in it.
In certain cases, the doctor also warns the patient to have the child soon if she is diagnosed with endometriosis.
The symptoms may get worse over time if the condition is left untreated and soon it may be difficult to conceive.