What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Tuberculosis (TB Symptoms)?
- Updated on: Jul 9, 2024
- 2 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019


Tuberculosis Symptoms (Symptoms of TB)
Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria that spread from infected person to healthy person via air. This happens when the infected person sneezes, coughs, sings or talks. If left untreated, it can be fatal.
The bacteria can live in the body of the host without making him/her sick. The person may or may not feel any obvious symptoms of the condition. When the bacteria are actively multiplying in the body, symptoms can be visible and make the person severely ill.
Symptoms of pulmonary and extra-pulmonary tuberculosis vary because of the location of the infection. This is described in detail here:
Symptoms of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
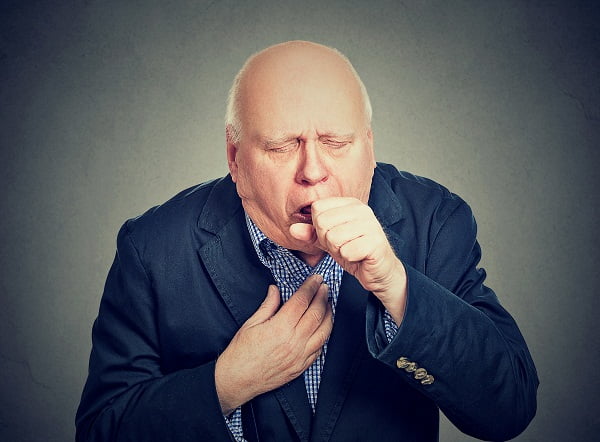
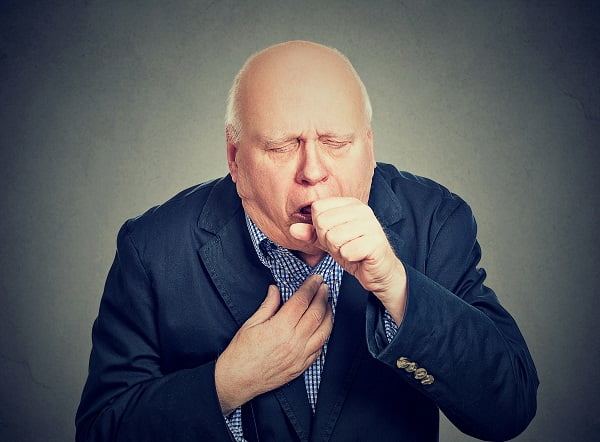
The bacteria that cause tuberculosis (M.tuberculosis) commonly grow in lungs. People already suffering from tuberculosis usually have following symptoms:
- a bad cough lasting for three or more weeks
- blood in sputum (hemoptysis)
- pain in the chest (while breathing, coughing and sneezing)
In addition, other symptoms are present, such as:
- fever (generally above 38°C)
- chills
- sweating at night
- unexplained weight loss
- decrease and loss of appetite
- fatigue and weakness
- shortness of breath
- pneumonitis (often fatal)
- usual feeling of illness and discomfort (malaise)
Symptoms of Extra-pulmonary Tuberculosis
Oxygenated organs of the body like kidneys, lungs, spines and bones are also affected by the condition. Symptoms may vary with the site of infection. For example:
Symptoms of Skeletal Tuberculosis
- spinal pain
- stiffness in back
- paralysis (possible)
Symptoms of Tuberculosis Meningitis
- mental changes
- severe headaches
- coma
Symptoms of Tuberculosis arthritis
- pain in joint
- hip and joint pain
Symptoms of Genitourinary Tuberculosis
- dysuria
- pain in the abdomen
- mass and lump formation (granulomas)
Symptoms of Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis
- non-healing ulcers
- abdominal pain
- difficulty in swallowing
- diarrhea
- blood in the stool
- malabsorption
Symptoms of Miliary Tuberculosis
- nodules formation in organs (resembling millet seed)
- widespread in other organs
symptoms of Pleural Tuberculosis
- pus in the pleural cavity (empyema)
- fluid in the pleural cavity (pleural effusions)
The symptoms of tuberculosis are very variable and depend on the location of the infection. It is difficult to diagnose tuberculosis on the basis of symptoms only as symptoms are usually overlapping.