What are the Symptoms of Epilepsy?
- Updated on: Jul 29, 2024
- 2 min Read
- Published on Feb 21, 2021

Signs and Symptoms of Epilepsy
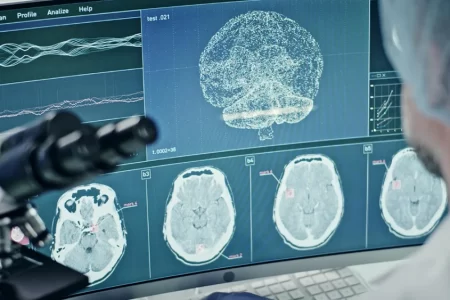
The most important symptoms of epilepsy are recurrent seizures. Seizures occur because of a sudden increase of electrical activity in the brain. There is an overload of electrical activity in the brain. This causes a temporary disturbance in the neurons. There are different types of seizures that may be experienced by a person who suffer with epilepsy. People with epilepsy can experience any type of seizure, although generally people have a consistent pattern of symptoms. Seizures can occur when the person is awake or asleep.
Symptoms generally vary depending on the type of seizure. In most cases, a person with epilepsy experiences the same type of seizure every time. In such cases, the symptoms are generally similar from episode to episode.
Doctors classify seizures as either focal or generalized, based on how the abnormal brain activity starts in the brain.
If you notice one or more of the following symptoms in an individual, it is important to meet a doctor, particularly if they repeat:
• a convulsion without fever
• short spells of temporary confusions
• intermittent fainting during which bowel or bladder control is lost
• unresponsive
• the person becomes stiff suddenly
• the person falls suddenly without any obvious reason
• loss of consciousness or awareness for sometime
• psychic symptoms or indications
• rapid jerking movements in arms, legs, or the body
• fear or panic for no apparent reason
• the person experiences a staring spell for some time and is unable to communicate
The following conditions need to be ruled out during diagnosis as they may show similar symptoms and are sometimes misdiagnosed as epilepsy:
• high temperature with symptoms similar to that of epilepsy
• fainting and loss of consciousness
• fear and panic
• nightmares
• recurring episodes of sleep during the day (narcolepsy)
• periods of extreme weakness (cataplexy)
• sleep problems
When to See a Doctor
You must seek immediate medical help if any of the following occurs:
• the seizure lasts more than five minutes
• a second seizure occurs immediately without much time gap
• consciousness does not return after the seizure stops
• you have a high temperature
• you are having a pregnancy
• you are a diabetic patient
• you have got any injury during the seizure
If you experience seizure for the first time, you should certainly get a medical help. Also, if the consciousness does not return even after 30 minutes, this may possibly be an emergency.