What Are the Symptoms of Prostatitis?
- Updated on: Aug 26, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019


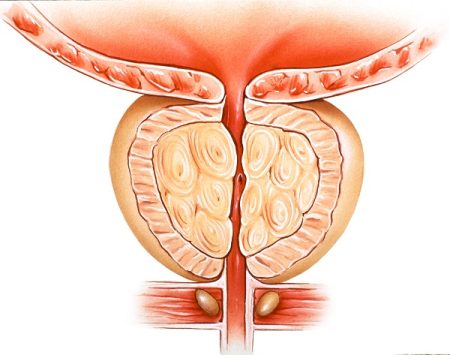
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that is present in all men right in front of the rectum and below the bladder.
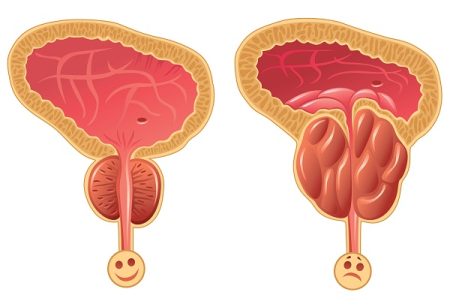
The main function of this gland is to produce a fluid that contains sperms. If the prostate becomes swollen and tender, the condition is called as prostatitis. The condition, however, is not “cancerous” and is different from an enlarged prostate. Prostatitis can be quite painful and troubling but can be treated. Following are the common symptoms of prostatitis.
What are the symptoms of prostatitis?
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating (dysuria)
- dribbling or hesitant urination
- Frequent urination, particularly at night (nocturia)
- Urgent need to urinate
- Cloudy urine
- Blood in the urine
- Pain in the abdomen region or groin area or in the lower back
- Pain in the area between your scrotum and rectum regions
- Pain or discomfort in the penis or testicles
- Pain during ejaculation
- Flu-like symptoms (occurs in case of bacterial prostatitis)
Types of prostatitis and their symptoms
Prostatitis is generally classified into four types. Each type has its own set of symptoms depending upon the causes. The details of each type with symptoms are given as:
Symptoms of Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
The urinary tract is made up of kidneys, bladder and tubes that pass between them. If bacteria find its way into the prostate gland, it may cause infection. The bacteria travel from urethra or rectum to prostate gland.
Symptoms of this problem are sudden and painful. These include:
- severe burning sensation during urination
- pain during urination and micturition (feeling of urinating)
- muscle and joint pain
- fatigue
- high fever
- chills
- pain around the base of your penis or behind your scrotum
- lower back pain
- feeling like you need to have a bowel movement
- trouble in urinating
- weak urine stream
- nausea and vomiting
- inability to empty bladder
Due to swelling in the prostate, the person may feel difficult to urinate. The person should notify the doctor if any of the above-mentioned symptoms last longer than a few days.
Symptoms of Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
This type of prostatitis is categorized with recurring of bacterial infection in the prostate gland. Symptoms may be minor between two attacks and the patient may even feel disease-free. This type of prostatitis is quite difficult to treat.
The infection is low-grade and can persist for weeks and months. Symptoms are not flu-like as in case of acute prostatitis.
Some symptoms are mentioned as:
- burning sensation during urination
- painful urination
- frequent urge to urinate (especially at night)
- urinary blockage (no urine comes out)
- trouble starting a stream of urine or having a weak stream
- low-grade fever, joint pains, and muscle aches
- urethral discharge and tender testes (or epididymis)
- pain during intercourse
- pain after you ejaculate (release semen at orgasm)
- pain in testicles, penis and bladder
- pain between genitals and anal opening
- lower back pain
- rectum pain
- a “heavy” feeling behind the scrotum
- blood in semen
- a UTI (urinary tract infection)
- Sexual dysfunction
This is more common in old men. Some men get it after they’ve had a urinary tract infection (UTI) or acute bacterial prostatitis.
Symptoms of Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS)
Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis is the most common form of prostatitis. The symptoms are somewhat common with Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis. However, no bacteria are found to trigger it.
The main sign of CPPS is pain that lasts more than 3 months in at least one of the following body parts:
- Penis (often at the tip)
- Scrotum
- Between your scrotum and rectum
- Lower abdomen
- Lower back
Stress and physical trauma are the main triggers of this type of prostatitis. Symptoms are listed below:
- burning sensation and pain during urination
- pain in the bladder
- trouble in ejaculation
- frequent urge to urinate (especially at night)
The condition leads to high sensitivity and sometimes may even cause nerve damage. Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis may negatively affect bladder, sexual functioning and bowel movement of the person.
Symptoms of Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis
Men who have this type of prostatitis have an inflamed prostate but show no symptoms. The condition is detected when the person is tested for other diseases like cancer.
This type of prostatitis can lead to infertility. Following are the symptoms of Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis:
- pain and trouble in urination
- strain on bladder muscles during urination
- frequent urge to urinate
- burning sensation during urination
- painful ejaculation
- painful bowel movement
- pain in lower back, pelvis and pubic area
- blood in semen
- sexual dysfunction in severe cases
The symptoms, though can be mild, should never be ignored. The disease is somewhat common but can be treated with proper medications and healthcare consultation. Read about treating prostatitis.
FAQs
Are urinary symptoms the only indicators of prostatitis?
No, prostatitis symptoms also include pelvic pain, sexual dysfunction, and flu-like symptoms. Urinary symptoms are just one aspect of the condition.
Can prostatitis cause back pain?
Yes, prostatitis can cause lower back pain, especially in cases of chronic prostatitis. It's essential to consider a range of symptoms for an accurate diagnosis.
Do all types of prostatitis cause the same symptoms?
No, symptoms vary based on the type of prostatitis. Acute prostatitis may present with severe symptoms, while chronic prostatitis may have milder and recurrent symptoms.
Can prostatitis symptoms be mistaken for other conditions?
Yes, symptoms like urinary urgency or pain may overlap with other conditions. A thorough medical evaluation is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
Are prostatitis symptoms age-dependent?
Prostatitis can affect men of all ages. While certain symptoms may be more common in older individuals, the condition can occur in younger men as well.