What Causes Prostatitis?
- Updated on: Jan 22, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
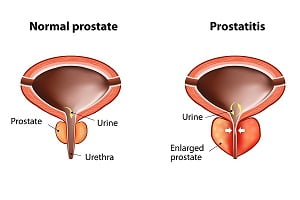
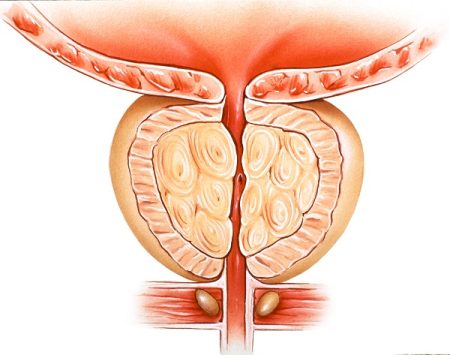
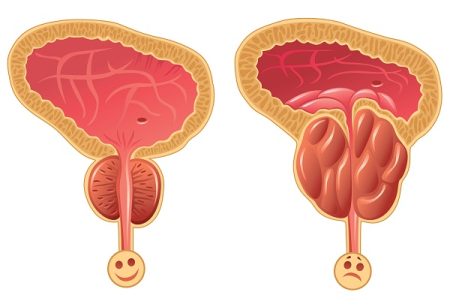
Prostatitis is infection and inflammation of the prostate gland. It is often difficult to treat and because of several forms of the disease, the root cause of this disease is yet to understand. There is a controversy among researchers about the onset of prostatitis.
Causes of Prostatitis
A person may develop inflammation in the prostate gland because of one or more reasons. There are many different causes of prostatitis. Listed below are the three main factors that can trigger prostatitis in a person:
- Bacterial infection
- Auto-immune response
- Neuromuscular or physical injury
Bacterial Infection
Chronic and acute prostatitis is caused by bacterial infection. Many different types of bacteria are associated with bacterial prostatitis. The most common ones are:
- E.coli
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- Enterobacter
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Proteus mirabilis
Even if the primary symptoms of prostatitis are treated, bacteria may continue to survive in the prostate gland. Urethritis or inflammation in urethra may be another reason for the growth of bacteria in the prostate.
Auto-immune response
Some researchers even suggest that chronic pelvic pain syndrome is a type of autoimmune disorder. The immune system is meant to protect the body from diseases and infectious agents. Nevertheless, at times, our immune system attacks healthy cells.
An autoimmune disorder is that condition in which body attacks its own healthy cells by mistake. This attack on self-cells can cause inflammation in the prostate gland and many other problems. These autoimmune disorders may be based on genes.
Following are some triggering factors of autoimmune diseases:
- a persistent viral or bacterial infection
- trauma to prostate or pelvic area (sports injury or vasectomy)
- family history of autoimmune disease
- overstressing
- prolonged use of antibiotics
- exposure to environmental toxins
The exact mechanism by which the autoimmune response leads to prostatitis is still unclear. This situation is quite challenging to diagnose as well as treat. The person gets flares which may disappear or improve on its own.
Neuromuscular injury
Any sports injury or trauma to the pelvic region can cause prostatitis. Pelvic trauma may be caused by:
- baseball or hockey impact during sports
- excessive riding of bicycle
- horse riding
- automobile accident that impacts pelvic area
- surgery of groin, pelvic area or prostate
- insertion of catheter
In addition to the above-mentioned reasons for physical injury to the groin area, some jobs also contribute to it.
Jobs that subject the groin/pelvic area to strong vibrations can lead to prostatitis. Heavy lifting with a full bladder can push the urine back into the prostate. The neuromuscular injury is not a result of one day but series of events that lead to pain and inflammation.
Other causes
The cause of prostatitis is not so obvious but can be detected by some tests. Researchers are not sure about bacteria being the main cause for the onset of disease as non-bacterial prostatitis is also reported by doctors.
Several theories suggest that initial trigger is sometimes present in the prostate itself that may cause inflammation. Keeping this in mind, following are the some other causes of prostatitis that are considered by researchers:
- uric acid disorder
- stones in prostate gland
- tumor in prostate
- non-cancerous growth in prostate
- urethral stricture
- allergy to some particular food
- yeast infection
- inflammation in urethra (urethritis) or other parts like testicles and vas deferens
- enlarged prostate
Am I at risk of prostatitis?
Though treatable, prostatitis is often not easy for diagnosis because of the wide variety of symptoms. The factors that increase the risk of sexually transmitted disease (STDs) and urinary tract diseases (UTIs) will eventually increase the risk of inflammation in the prostate gland and thus cause prostatitis.
The risk factors for prostatitis include:
- using urinary catheter
- not drinking sufficient amount of fluids
- multiple sexual partners
- unprotected intercourse
- history of prostatitis
- hereditary that makes a person susceptible to prostatitis
- inflammation in testicles
- HIV and AIDS infection
- psychological stress
- enlarged prostate
- frequent bladder infection
Timely consultation with the healthcare professional and taking care of your health can help you avoid as well as treat prostatitis.
FAQs
Is bacterial infection the only cause of prostatitis?
No, while bacterial infection is a common cause, prostatitis can also result from non-bacterial factors like pelvic muscle dysfunction or autoimmune issues.
Can sexually transmitted infections (STIs) lead to prostatitis?
Yes, some STIs can contribute to prostatitis. Gonorrhea and chlamydia are examples of infections that may cause inflammation in the prostate.
Are lifestyle factors linked to prostatitis development?
Yes, factors like stress, sitting for prolonged periods, and inadequate fluid intake can contribute to prostatitis. Lifestyle modifications can play a role in prevention.
Can prostatitis be hereditary?
While there's no direct hereditary link, genetic factors may contribute to an individual's susceptibility to inflammation, potentially increasing the risk of prostatitis.
Does age influence the development of prostatitis?
Prostatitis can affect men of all ages, but age-related changes in the prostate may increase the risk. It's not exclusive to any specific age group.