What Causes Tuberculosis (TB) and What are the Risk Factors for Tuberculosis?
- Updated on: Jul 9, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
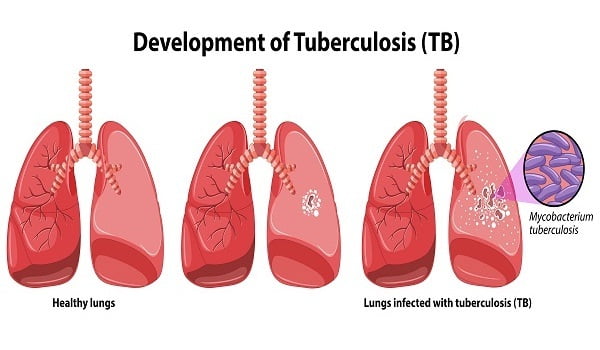
Bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the causative agent of tuberculosis infection in humans. These are slow growing and oxygen utilizing bacteria that can grow in body cells.
How do the TB bacteria spread the disease?
The bacterium has a cell wall (covering) that helps to protect it from body’s immune system and defense mechanism. It is an intracellular parasite. M. tuberculosis that escapes from body’s immune system may spread the infection to other organs of the body via blood and lymphatic system.
The organs that are well oxygenated like lungs, kidneys and bones are more susceptible to risk. Initially, the bacteria stay in dormant state (latent stage) but as the infection advances, the bacteria gets active.
The spread of tuberculosis from the infected person to healthy person is through microscopic droplets released by the former in the air. This happens when the person with active untreated infection coughs, sneezes, talks, sings, laughs and spits. Though the disease is contagious, but it is not so easy to catch.
Infections are more likely to happen if we live or work with an infected person rather than the stranger. It spreads like common flu and cold but not equally fast.
Tuberculosis Causes and Risk Factors (TB Causes)
Following are some causes of tuberculosis:
- HIV/AIDS
- Drug-resistant strains
- Weak immune system
- Lack of medical care
- Drug and tobacco addiction
- Working and living place
HIV/AIDS
In the past few years, the number of cases of tuberculosis has increased dramatically. This is because of the spread of HIV/AIDS virus.
HIV infection suppresses the immune system and makes it difficult for the body to control the tuberculosis infection. Thus, persons suffering from HIV/AIDS are more prone to get active tuberculosis.
Drug-resistant strains
Drug-resistant strains of any disease are considered the serious threat to the human population. Some tuberculosis germs have the ability to survive antibiotic action and thus survive the treatment. This ability gets transferred to the bacterial progenies.
These strains emerge when an antibiotic fails to kill 100% of its target bacteria. The surviving bacteria become resistant to that particular drug and other related drugs. In studies, it was found that tuberculosis bacteria are resistant to common treatments like isoniazid and rifampin.
Some strains have developed resistance to the following antibiotic:
- Fluoroquinolones
- Amikacin
- Kanamycin
- Capreomycin
Often these drugs were used to treat resistant strains.
Weak immune system
If the immune system is healthy, it can fight tuberculosis infection. However, when the immune system is weak, it cannot mount an effective defense against the disease. Following are the situations that can suppress the immune system:
- HIV/AIDS
- Kidney diseases
- Certain Cancers
- Cancer treatment
- Organ transplantation drugs
- People undergoing immune-suppressive therapy
- Diabetes
- Drugs for rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease and psoriasis
- Malnutrition
- Silicosis
Lack of medical care
People living in remote areas having low annual income may not have access to advanced medical technologies and diagnostic methods used for the prevention of tuberculosis.
Homeless and poor people are more prone to get this condition. Generally, these people have already weakened immune system because of poor health and unsanitary conditions; lack of medical aid makes it worse.
Drugs and tobacco addiction
Drugs and alcohol are known to weaken the immune system of the person. Thus, they make the person more susceptible to this condition. Chewing tobacco greatly increases the risk of tuberculosis.
Working and living place
Regular contact with already infected people increases the chances of getting tuberculosis. People living or working in areas like immigration centers, nursing homes and prisons are at higher risk. This is because of the overcrowding and poor ventilation of the area.
Who is at risk of TB (Tuberculosis)?
Anyone can get this condition, but following people are at greater risk:
- People living in countries and areas with high level of tuberculosis infection
- Prolonged exposure to already infected person
- People living in crowded condition
- People with HIV/AIDS
- People having immune-compromised condition
- People with weak immune system
- People with poor and unhealthy lifestyle
- People addicted to drugs and alcohol
- People recently infected with tuberculosis and not treated
- Very young and very old people