What is Asthma?
- Updated on: Jul 9, 2024
- 3 min Read
By
- Published on Sep 27, 2019
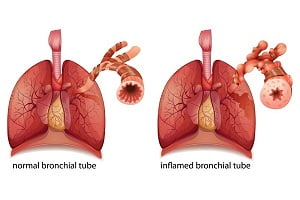
Overview of Asthma
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects the airways in the lungs. The airways are also known as bronchial tubes. Their main work is to allow air to come in and move out of the lungs.
Asthma is a disease that causes inflammation of the airways making them swollen. This may result in the sensitive inner walls of the airways to react strongly when something triggers. The airways react to the triggers by getting narrower which make it difficult for the air to move in and out of the lungs. And then gradually the person experiences symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath and chest tightness.
The swelling can worsen the condition of the airways, making them even narrower. This condition also makes cells in the airways to produce more mucus than usual that further narrows the airways. These series of reactions can result in asthma symptoms. Symptoms occur every time the airways are inflamed.
Who Gets Asthma?
Normally, asthma develops during childhood, but it can affect at any age. People are more likely to have the condition if:
- they have allergies
- their parents have asthma
- close family members have asthma
In childhood, boys are more likely to get asthma than girls, and in adulthood, women have greater chances of asthma than men. Childhood and teenage phase can put at higher risk with respect to asthma.
Types of asthma
Broadly asthma is classified into two types: allergic and non-allergic asthma.
Allergic asthma
Allergic asthma is caused by exposure to an allergen like pollen, dust mites, or mold (a kind of fungus). It is the most common type of asthma. Approximately 90 percent of kids and 60 percent of adults are affected by this type of asthma.
Non-allergic asthma
Non-allergic asthma is caused by factors other than allergens such as stress, exercise, illnesses (like a cold or the flu, or exposure to extreme weather) and some medications. It is a chronic condition and it usually occurs after midlife because respiratory tract infections are seen after midlife only.
Symptoms of asthma
Common symptoms of asthma include coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing (a whistling sound in the chest while breathing, especially when exhaling) and chest tightness. All symptoms of asthma are serious and can become deadly if not treated at the time. Read more about asthma symptoms.
Triggers of asthma
Asthma symptoms appear when the patient gets exposed to a trigger (a factor that makes the airways inflamed). The trigger may cause swelling, mucous production and narrowing of the airways.
Some of the most common triggers of asthma are pollen, chemicals, extreme weather changes, smoke, dust mites, stress and exercise. Read more about causes and triggers of asthma.
Diagnosis of asthma
Diagnosis of asthma is done in a series of steps performed one after the other. These steps include:
- Taking a detailed medical history of the patient.
- A physical exam to know about symptoms and to rule out other health problems.
- Lung function tests to determine how much air moves in and out while breathing.
- Chest or sinus X-ray.
The results of the above tests determine the type of asthma a patient is suffering from. Based on the results, severity and type of asthma, a treatment plan is made.
Treatment for asthma
An allergist is a person who treats asthma and he helps the patient to make a treatment plan based on the diagnosis of the condition. Treatment plan involves medications to treat the condition and prevention measures to avoid the triggers as much as possible.
Read more about asthma treatment.
Prevention of asthma
The best way to prevent an asthma episode is to follow the treatment plan. Following things can be done to prevent the disease:
- Acquiring knowledge about the triggers.
- Avoiding triggers.
- Taking allergy and asthma medicines on time.
- Taking quick-acting medicine as soon as the first symptom is noticed.












