What Is Crusted Scabies (Norwegian Scabies): Symptoms, Medicines, Treatment
- Updated on: Jan 27, 2025
- 6 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
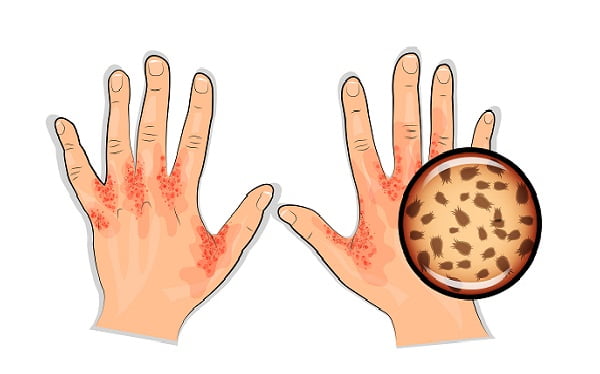
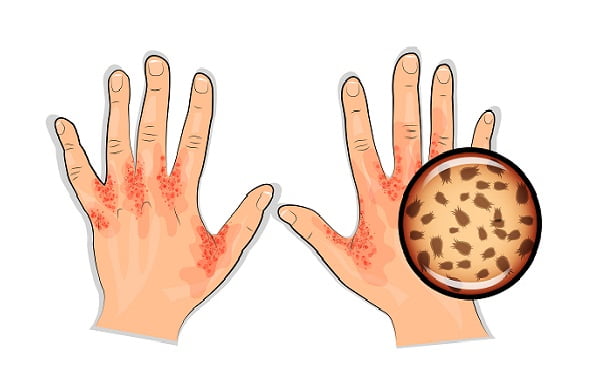
What is crusted scabies?
Crusted scabies, also called Norwegian scabies, is a destructive form of scabies that can occur in some people who are immune-suppressed (have a weak immune system), or physically challenged. It is also called Norwegian scabies.
Crusted scabies, also called Norwegian scabies, is a destructive form of scabies that can occur in some people who are immune-suppressed (have a weak immune system), or physically challenged. It is also called Norwegian scabies. In environments where crusted scabies has been identified, thorough cleaning and disinfection protocols are crucial. Using EPA Registered Disinfectant Wipes can help to effectively sanitize surfaces and reduce the risk of transmission in such settings.
Persons with crusted scabies have thick and hard crusts of skin that contain large number of scabies mites and eggs. Persons with crusted scabies are very contagious to other persons and can spread the infection easily both by direct contact with skin and by contamination of items such as their clothing, bedding, and furniture.
You must maintain a strict hygiene regimen to effectively manage crusted scabies along with medical treatment. Any kind of personal item, including clothing, bedding, and furniture, should be disinfected regularly. Using an EPA-registered disinfectant can significantly reduce the risk of scabies transmission in communal environments, particularly in nursing homes, hospitals, or households with multiple individuals.
People who suffer with crusted scabies may not show the usual signs and symptoms of common scabies such as rashes or itching. In fact, people with this type of scabies may not experience a lot of itching as is found in common scabies. But people need quick treatment for their infestation to prevent outbreaks of scabies.
How are crusted scabies different from classical scabies (common scabies)?
Norwegian scabies, or crusted scabies, is different from the classical common scabies. There is a problem with the immune response to the mites in this type of scabies which causes the infestation of an individual with thousands of the mites.
In almost all cases, crusted scabies affects people with a compromised or weak immune system and is more common in aged people, who are mentally or physically disabled, and in patients with AIDS, lymphoma, or other conditions that reduce the ability of your immune system.
It may spread all over your body. It can affect your elbows, knees, palms, scalp, and soles of the feet in the beginning which will eventually assume a wart-like appearance.
The lesions in crusted scabies often predispose to the development of secondary infections.
Is crusted scabies a common disease?
This type of scabies is rare and therefore its diagnosis and treatment (cure) is a challenge, as the common drugs used against scabies are not satisfactory. Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis shows uncontrolled proliferation due to the inability of an individual to mount an immune response to the scabies mite.
Risk factors of crusted scabies: Who can get crusted scabies?
These types of people are at risk of getting crusted scabies:
- People with certain nutritional disorders, infectious diseases, leukemia, weak immune system (such as in people with AIDS).
- People who have mental or neurological disorders.
Symptoms of crusted scabies
Common crusted scabies symptoms are:
Small bumps and blisters can develop in the webs between your fingers, on the wrists, the backs of the elbows, in the groin region, on your knees, and on the buttocks.
Men can sometimes get pimples-like things on their penis as a result of crusted scabies. But remember not every bump on the skin is a scabies infestation.
Early Detection and Prompt Treatment are Necessary
Early detection and treatment of crusted scabies are essential to prevent severe complications that may emerge from this condition such as secondary bacterial infections, spread to other individuals, and long-term skin damage. If you think you might have this infection, you should seek immediate medical attention so that the treatment can start early.
Treatment of crusted scabies
Treatment options in crusted scabies are limited and are unsatisfactory. Most medicines such as permethrin, benzyl benzoate, and gamma benzene hex chloride or ivermectin, that are generally used for classical scabies do not show satisfactory results as they fail to penetrate the thick and adjoined scales and crusts due to crusted scabies.
Norwegian scabies is treated with topical permethrin cream (Elimite) and the oral medication ivermectin (Stromectol). Treatment of crusted scabies can require oral medications along with multiple applications of a scabicide cream unlike the classical scabies treatment.
Dilute ammoniated mercury (5%) is safe and effective in the treatment of crusted scabies. Galenicals can also be helpful. The advantage of galenical medicines is that they can be titrated and tailor-made to suit the patient needs by varying the concentrations of the various ingredients.
Medicines for the treatment of crusted scabies
- Lindane also known as gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane is used as an insecticide. Lindane in humans is used in lotions, creams, and shampoos to treat scabies and lice. But it is not generally recommended due to its toxicity.
- Ivermectin and topical medications such as permethrin are generally used to treat crusted scabies.
- Antibiotics may also be required to treat secondary bacterial infestations that arise from scratched skin.
- Permethrin belongs to a class of drugs known as pyrethrins. Permethrin works by paralyzing and killing the mites and is used to treat crusted scabies.
Pregnant women are treated for scabies only if diagnosed by biopsy.
Other than the above mentioned medicines, there are some additional medications that have been used in the treatment of scabies such as the following:
- 25% Benzyl benzoate lotion
- 0.5% Aqueous malathion lotion
- 2-10% Precipitated sulphur ointment
Natural remedies (galenicals) in the treatment of crusted scabies
Galenical preparations for crusted scabies include:
- Salicylic acid 3%
- Unguentum hydrargyrum ammoniatum dilutum (Ung HAD) 5%
- Liquor picis carbonis 7%
Purified white vaseline to make 100% is also recommended to be applied on the affected areas twice daily.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Recent research studies suggest that new and emerging treatments may offer some hope for people who suffer with scabies for a more effective and holistic management of crusted scabies. Research into newer anti-scabies agents and immune-modulating therapies is ongoing, which may provide better results in patients who do not respond to conventional treatments.
New drugs with a longer half-life or with ovicidal properties are being developed that would be revolutionary for the treatment of scabies. New anti-scabies drugs are currently being developed and trialled on porcine hosts, as pigs and humans have similar genetics, skin physiology, and immunology. Pre-clinical trials revealed a single dose of moxidectin, a highly lipophilic macrocyclic lactone, or afoxolaner, a novel acaricide, to be more effective than two doses of ivermectin[1].
Several research gaps are identified by experts as priorities for effective scabies control in endemic communities. These include the need for standardised approaches, newer diagnostic tests, and digital technologies to improve diagnosis of scabies. The development of a simple, low-cost rapid assessment tool is also highlighted as key priority during recent research about this disease[2].
Treating Close Contacts and Preventing Re-infestation
While treatment of person with scabies early on is necessary, it is also important that everyone in close contact with the infected person, including household members and sexual partners, receive treatment at the same time. This reduces the risk of re-infestation and further spreading of the mites. You must ensure that all contaminated clothing and bedding and other items that have been shared are thoroughly cleaned and treated to prevent recurrence and spread. Wash all clothing, towels, and bedding used next to the skin during the three days before starting the treatment regimen. This should help in preventing possible re-exposure and reinfestation.
Who needs crusted scabies treatment?
In addition to the contagious person (patient), treatment of crusted scabies is also recommended for household members and sexual contacts, particularly those who have had prolonged direct skin contact with the contiguous person carrying the scabies disease.
All members should be treated at the same time to prevent re-infestation. Crusted scabies may sometimes be sexually-acquired in adults, but is rarely found in children.
To prevent the infestation, treatment should be done to remove contamination by washing the bedding, clothing, and towels used by persons or their household or by their sexual and close contacts in hot water and drying in a hot dryer, by dry-cleaning, or sealing in a plastic bag for at least 72 hours.
Scabies mites survival is not more than 2 to 3 days when away from human’s body.
Crusted Scabies and Comorbidities
Crusted scabies is often associated with individuals suffering from other comorbid conditions such as malnutrition, neurological disorders, or HIV/AIDS. These conditions compromise your immune system, which makes it difficult for your body to fight with the scabies infestation. The treatment plans your doctors recommend should consider underlying health issues for more effective management.
Trusted Sources
- Emily Welch, Lucia Romani, and Margot J. Whitfeld, “Recent Advances in Understanding and Treating Scabies,” Faculty Opinions, March 11, 2021.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8009191/ - Elke Mitchell, Miranda Wallace, and Justine Marshall et al., “Scabies: Current Knowledge and Future Directions,” Frontiers in Tropical Diseases, July 23, 2024
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/tropical-diseases/articles/10.3389/fitd.2024.1429266/full











1 Comment
I like what you guys are up also. Such intelligent work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my web site :).