What Is Lupus?
- Updated on: Jun 5, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019

Immune System and Lupus
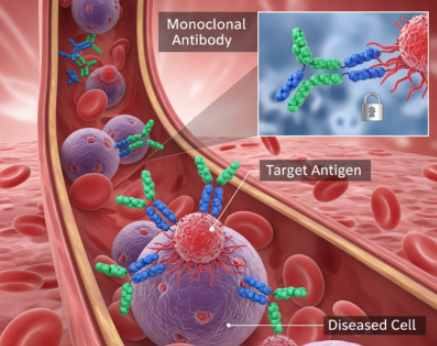
Our immune system is one of the main systems in the body. It strives to protect our body from various bacteria, germs and viruses by producing antibodies against any foreign body. These antibodies are mainly produced by white blood cells (WBCs or B-lymphocytes) which are a part of our immune system.
Lupus is a common name given to a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the immune system of a human becomes hyperactive and start killing (attacking) healthy cells. It can also be described as malfunctioning of the immune system. Basically, with lupus, the immune system is not able to differentiate between healthy cells (or body cells) and foreign invader cells.
Antibodies are produced against healthy cells and tissues which cause inflammation, pain and damage in various parts of the body. These antibodies so produced are called as “auto-antibodies” and cause inflammation in various organs of the body. These auto-antibodies circulate in blood but leaky (permeable) nature of cell boundary lets them in. These auto-antibodies then attack DNA present in the nucleus of a cell. This is the reason why some organs show symptoms very quickly while others do not.
“Antinuclear antibody” (ANA) is the most common type of autoantibody produced by the immune system in people with lupus and it reacts with parts of the nucleus (DNA center or command center of the cell) present in the cell.
Some people have a genetic tendency to develop lupus. Also, it may be triggered by infections, drugs and sometimes by sunlight.
Type of Lupus
Lupus is a chronic inflammatory disease and the symptoms of this disease can affect any parts of the human body including joints, blood cells, brain, heart, lungs and skin. Lupus, in general, is categorized in four types:
- Systemic
- Discoid
- Drug-Induced
- Neonatal
These lupus types are briefly elaborated below:
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
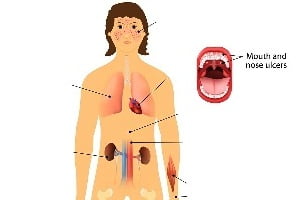
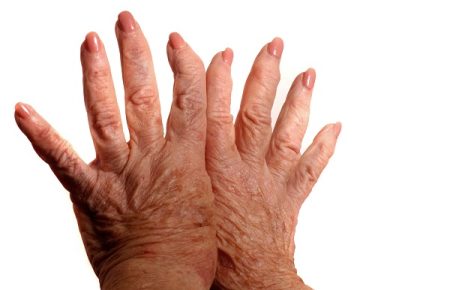
It is the most common type of lupus and is quite often mistaken as a skin disease. The symptoms of this condition vary from person to person. Common symptoms include swelling and pain in joints, hair loss, swollen lymph nodes, tiredness and a red rash which is most commonly present on the face. A person suffers from “flares” when symptoms are most recognizable.
Though the cause of lupus is not clearly known, hormones, environmental conditions and genetic factors are supposed to be the reason. Female sex hormones, Vitamin D deficiency, sunlight and smoking are believed to increase the risk.
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE)
It is a chronic skin condition which causes sores and scars on face, ears, scalp and sometimes on other body parts. Crusty abrasions (or wounds) with red inflamed patches appear on the skin. The center part of these wounds may appear lighter in color with a rim darker than normal skin. It can be of three types: localized, generalized or childhood discoid lupus.
Drug-induced Lupus Erythematosus (DIL or DILE)
It is somewhat similar to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and is caused by the use of certain drugs that induce an autoimmune response. Highest numbers of cases are reported after the use of hydralazine, procainamide and isoniazid. Apart from these three, there are about 38 known drugs that induce DILE.
Symptoms are more or less similar to that of SIL like swelling and pain in joints, hair loss, swollen lymph nodes and tiredness which usually recede after discontinuation of drugs. Serositis is a symptom specific to DILE, in which thinning of heart and lung lining occurs.
Neonatal Lupus Erythematosus
Neonatal Lupus Erythematosus refers to the occurrence of SLE in newborn babies. It develops because of genetic reasons (such as mother suffering from SLE). Symptoms include DILE-like abrasions and abnormalities like complete heart blockage. Neonates do not have skin abrasions at birth but develop within a week of birth.
Lupus can be sometimes difficult to diagnose as its signs and symptoms imitate those of skin diseases. The most common and distinctive sign of lupus is a facial rash that resembles butterfly unfolding its wings across both the cheeks. This symptom is seen in most but not all of the cases. Read more about lupus symptoms.
Treatment helps to control the symptoms but there is no cure for lupus. Read here about lupus treatment.
What do surveys say about lupus?
About 20% of the people diagnosed with lupus have either a parent or sibling having the same condition. Around the world, about 5 million people have some or the other form of lupus and 70% of these people are diagnosed with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Lupus occurs from infancy to old age but is majorly seen in people in age group of 15-40. A report says that females are up to six to seven times more prone to develop lupus as compared to males in the United States and the United Kingdom. However, according to another survey from the Lupus Foundation of America, more than 70% of American people who are at high risk of developing this condition have not either heard about Lupus or don’t know anything about it.