What Is the Treatment for PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)?
- Updated on: Jul 9, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Sep 27, 2019
There is no cure for polycystic ovary syndrome but the symptoms can be managed. Treatment options vary from person to person because of the wide range of symptoms. The main treatment options are enlisted here.
PCOS treatment
- Lifestyle changes
- Medications for irregular periods, fertility issues and unwanted hair growth
- Surgery
- Hormone therapy
- Acne treatments
- Regular checkups
Lifestyle Changes
Overweight and obese women are at high risk of developing PCOS and other long-term health complications. PCOS can be improved by improving lifestyle and by losing excess weight.
Experts say that weight loss of 5% can lead to a significant improvement in PCOS symptoms. By calculating Body Mass Index (BMI), a woman can know whether she lies in the healthy or unhealthy category.
A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered healthy. Weight can be shed by exercising regularly and having a healthy balanced diet. The diet should normally include plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole foods and cereals.
Dietary advice can be taken from any general physician. Consider quitting smoking as it increases the level of androgens.
No single diet or activity plan is known to work better than another in helping women with PCOS. Some specific changes like lowering calorie diet, losing weight and getting more physically active can help a lot in the symptoms of PCOS.
Medications
A number of medications for managing the symptoms of PCOS are commercially available. Some of them are described here:
Irregular or no periods in PCOS
The doctor may recommend contraceptive pills to induce regular periods. An intermittent course of progesterone tablets to induce periods is also suggested. It is usually given every three to four months but can also be taken monthly.
These medications reduce the risk of developing endometrial cancer associated with not having periods. Other hormonal methods of contraception like intrauterine system (IUS) help in reducing the thickness of womb lining. However, these are not efficient in causing periods.
Fertility issues in PCOS
With timely diagnosis and proper treatment, most of the women are able to conceive a baby even with PCOS. Majority of women suffering PCOS can be treated with a short course of the tablet taken at the start of each cycle.
If medications do not work, the doctor may also suggest injections and IVF treatments at the best IVF center. Clomifene, a medicine, is usually first treatment recommended for women with PCOS trying to conceive. It stimulates the monthly release of an egg from the ovaries. An alternative to clomifene is metformin, which is often used to treat type-2 diabetes. However, it can also lower insulin and blood sugar levels in women with PCOS.
Stimulating ovulation and encouraging regular monthly periods lowers the risk of miscarriage. However, there might be some side effects of these medications such as nausea, vomiting and stomach pain.
Letrozole and tamoxifen are sometimes used to stimulate ovulation instead of clomifene. These medications can also be used for treating breast cancer.
However, if the woman is still unable to conceive, gonadotrophins are given as injections. This might increase the risk of overstimulation of ovaries and multiple pregnancies. An alternative treatment to avoid these complications is to undergo a surgical procedure called as laparoscopic ovarian drilling.
The fertility specialist will check if the fallopian tubes aren’t blocked for further treatment.
Unwanted hair growth and hair loss in PCOS
PCOS bring outgrowth of hair on face and body. Along with this, the woman also suffers from loss of hair from the scalp. Medications to control excessive hair growth and hair loss are enlisted here:
- combined oral contraceptive tablets (Co-cyprindiol, Dianette, Marvelon and Yasmin)
- cyproterone acetate
- spironolactone
- flutamide
- finasteride
Some of the above-listed medications work by blocking the effect of male hormone while some work by suppressing their production by ovaries.
Eflornithine, a cream can also be used to slow down unwanted facial hair growth. It doesn’t remove any hair but slows down the growth. For removal of hair from the face and the body, a woman can opt for laser hair removal methods.
Shaving, bleaching, plucking, waxing, and using depilatories are some of the more common ways of removing or hiding unwanted hair.
Treatment of Other symptoms
To improve other symptoms, following are the treatment options:
- Orlistat for weight loss
- Statins for improving cholesterol in blood
- Acne treatment creams
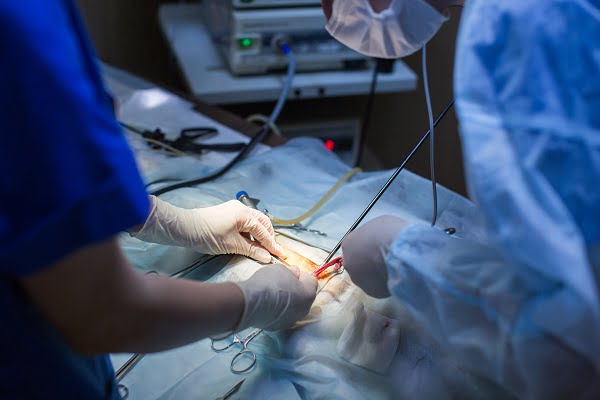
Surgery
A minor surgery is performed for testing fertility problems if medications don’t work. The surgery is called laparoscopic ovarian drilling (LOD).
Under general anesthesia, the doctor makes a small cut in the lower abdomen and passes a long thin microscope called laparoscope into the abdomen. The ovaries are then surgically treated using heat and laser to destroy the androgen-producing tissues.
Surgery also lowers the level of testosterone and luteinizing hormone. This restores the normal functioning of ovaries by correcting hormone imbalance.
Hormone Therapy
If weight loss alone doesn’t start ovulation, the doctor might suggest hormone therapy. Hormone therapy is also known to help with male-pattern hair growth and acne.
Birth control pills, patches, or vaginal rings are the most commonly prescribed forms of hormone therapy. Aldactone, an androgen lowering medication is often used and combined with hormonal birth control medicines. This helps with hair loss, acne, and male-pattern hair growth on the face and the body.
However, hormone therapy is not beneficial for other risks associated with heart, blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes. Exercise and a healthy diet are very important in PCOS treatment.
Acne Treatments
Commonly retinoid, antibacterial agents, and antibiotics are used to treat acne. These products are available as pills, creams, or gels. The specific treatment depends on the severity of the acne.
Asretinoids can cause birth defects in an unborn child. These options should not be used if a woman is planning to conceive.
Regular Checkups
Regular checkups are important for diagnosing any PCOS complications like uterine cancer, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease (e.g. coronary heart disease) and diabetes.