What Is the Treatment for Rosacea?
- Updated on: Jul 29, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Apr 19, 2021

Treating your rosacea symptoms
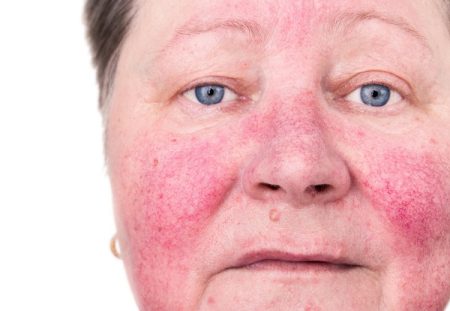
Although rosacea cannot be cured completely, the available treatments can help ease the symptoms. The disease generally requires a long-term treatment. People may have certain periods when the symptoms improve and they can stop treatment temporarily during these periods, which can cause the symptoms to become worse.
Treatment options depend on the symptoms that cause most trouble.
There are many treatment options for rosacea depending on the severity and extent of your symptoms. Your doctor may recommend antibacterial medication for infection, topical creams, antibiotic tablets, and therapies such as pulsed-light therapies and photodynamic therapy.
Self-help measures
There are several things that you can do on your own to help ease the symptoms of rosacea.
- avoid things that trigger your symptoms – such as cover yourself or apply cream in the sun to avoid sun exposure
- keep your eyelids clean – if your eyelids become inflamed due to rosacea, you should keep them clean
- take care of your skin – use products that are suitable for your sensitive skin
Medications
The medication your doctor prescribes depends on the signs and symptoms causing the trouble. Prescription drugs for rosacea may include such as:
Medications to reduce redness (topical treatments for rosacea)
Brimonidine (Mirvaso) helps in reducing redness. It is applied as a gel to the skin. It shows immediate results. You may feel better within 12 hours after application.
The medication has to be applied regularly to maintain the improvements as its effect is not permanent.
Azelaic acid and metronidazole are other topical treatments but their affects usually do not appear in the first five weeks.
You’ll have to apply these topical creams or gels once or twice a day. These should not enter in your eyes or mouth. It may take several weeks for these drugs to show any significant improvement in the symptoms.
This medication can cause side effects such as a burning sensation, itchiness, and dry skin.
Oral Antibiotics for rosacea
Antibiotics help fight inflammation in rosacea. Your doctor may presscribe doxycycline, which is an antibiotic consumed as a pill for moderate to severe rosacea with bumps and raises. Tetracycline, minocycline are other drugs that can be used but their effectiveness is not established.
Side effects of these medications include:
- feeling of being sick
- diarrhea
- loss of appetite
- bloating
- indigestion
- abdominal pain
These medicines are taken once or twice a day. You may not notice a significant improvement in your symptoms in the first few weeks.
Oral Isotretinoin (Amnesteem, Claravis)
Isotretinoin is a medicine that is often used to treat severe acne. But at lower doses, it’s sometimes used to treat rosacea also.
In case of severe rosacea, your doctor may suggest isotretinoin. It is a strong drug that can cause a range of side effects, and is not recommended during pregnancy as it can cause serious pregnancy complications and birth defects.
Other possible side effects are:
- dryness of skin
- muscle or joint pain
- back pain
- blood in urine (haematuria)
- headache
- inflammation of eyelids
- conjunctivitis
- changes in the mood
Laser and intense pulsed light (IPL) treatment
The therapy is sometimes used to treat redness and visible blood vessels (telangiectasia). This may improve flushing symptoms also.
Laser machines are used to produce narrow beams of light that target the visible blood vessels in the skin. The heat from these lasers damages the dilated veins and shrinks them so they’re no longer visible. Scarring is minimal and generally there is no damage to the skin.
Laser treatment can be painful, but usually people do not need anesthesia.
Common side effects of laser treatment are:
- Development of bruising
- Swelling and redness of the skin
- Sometimes blisters may develop, though this is rare
- One can rarely develop infection
These side effects usually disappears within a few weeks, but if it becomes infected you may require antibiotics.
Treatment of thickened skin (rhinophyma) due to rosacea – Plastic Surgery
In severe cases, rosacea can cause thickening of the skin, in particularly around nose.
Your doctor may refer you to a plastic surgeon to discuss how the appearance of your skin can be improved.
Surgical options are available to remove extra tissues developed around nose due to inflammation and reconstruct the skin of your nose.
For example, laser technology or abrasive systems may be used for the surgical correction.
Treating ocular rosacea (eye problems)
If rosacea causes eye complications, you may require further treatment for this condition.
Your doctor may ask you to use lubricating eye drops or ointment if you have dry eyes, or oral antibiotics if you have blepharitis.
You may be referred to an ophthalmologist for further assessment and treatment if the symptoms do not improve soon.