Browsing: Enlarged Prostate Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Enlarged Prostate
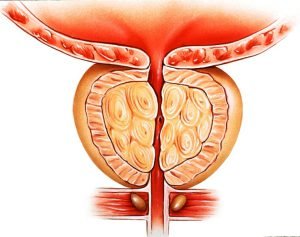
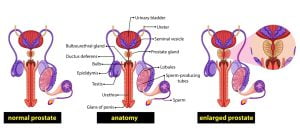
The prostate gland is located between the bladder and the penis, in-front of the rectum and is about the size of a walnut. The prostate is divided into these anatomical zones: central zone, transitional zone and peripheral zone. The arterial supply to the prostate comes from the prostatic arteries and venous drainage of the prostate is via the prostatic venous plexus. Several diseases and conditions associated with prostate are prostate cancer, enlarged prostate, prostatitis, hematuria, etc. Enlarged prostate is the swelling of prostate gland. Risk of enlarged prostate increases with age and causes difficulty in urination, dribbling of urine, UTI’s, etc.
The prostate gland is a part of male reproductive organ which rests on the bladder and surrounds the urethra. The healthy prostate gland is capable to produce some of the fluid in semen that carries sperm during ejaculation. In case of enlarged prostate, the flow of urine from the bladder through the urethra (the tube through which urine passes out of the body) is blocked. Due to an increased hormonal activity, over-growth of prostate cells leads to prostate enlargement which puts a pressure on the urethra and narrows it. This ultimately increases the chances of urine infection, kidney stones, bladder stones, etc.
ADVERTISEMENT